Keywords from D to P
You can check the part 1 and part 3 before or after reading this one
D-E
F-M
N-P
D
decltype: Inspects the declared type of an entity or the type and value category of an expression. See: cppreference/decltype
C++
template<typename T>
auto foo(T t) -> decltype(auto) {
return std::string();
}
int main() {
auto x = 10.5;
if (std::is_same_v<decltype(x), double>) {
std::cout << "Same types";
}
auto l = []() -> decltype(auto) {
return 10;
};
}default: It can be used in two different contexts. First, as a clausule in a switch statement to be called in the case the value we try to match it’s not supported by any case. And second, to default initialize special member functions. Since C++20 it could also be used for default comparisons. See: cppreference/default
C++
class S {
public:
S() = default;
~S() = default;
int x = 5;
};
int main() {
S* s = new S();
switch(s->x) {
case 1:
std::cout << "1";
break;
default:
std::cout << "10";
}
}delete: It can be used in two different contexts. First, to release memory after an allocation. And second, to delete special member functions. See: cppreference/delete
C++
class S {
public:
S() = delete;
};
int main() {
int* x = new int(10); // Allocates 4 bytes of memory in the heap.
delete x; // Release those 4 bytes of memory.
S* s = new S(); // error: use of deleted function 'S::S()'.
}do: Only used in ado-while-loopto always perform the first iteration. See: cppreference/do
C++
do {
std::cout << "First and only iteration"
} while(false);double: Floating point number with size of 64 bits (8 bytes). Matches IEEE-754 binary64 format if supported. See: cppreference/double
C++
double x = 10.0;
std::cout << sizeof(x); // 8dynamic_cast: Safely converts pointers and references to classes up, down, and sideways along the inheritance hierarchy. It is done at runtime and returnsnullptrif the action could’t be done andstd::bad_castif you try to cast a reference type. See: cppreference/dynamic_cast
C++
struct Base
{
Base() {}
virtual ~Base() {}
};
struct Derived : Base
{
Derived() {}
virtual void Foo() {
std::cout << "Derived::Foo()\n";
}
};
int main()
{
Base* b = new Derived();
if (Derived* d = dynamic_cast<Derived*>(b); d != nullptr)
{
d->Foo();
}
}
// Output
Derived::Foo()E
else: Part of the if statement that executes when the if clausule is not satisfied. See: cppreference/else
C++
if (false) {
} else {
std::cout << "If statement is false";
}
// Output
If statement is falseenum: Enumeration of values for a certain type. If used with the class specifier, our enumeration will be scoped and the values enumareted inside could be repeated. We can also specify the type of our enumeration See: cppreference/enum
C++
enum class e : int {A, B, C};
enum class s : char {A = 'A', B = 'B', C = 'C'};
int main() {
std::cout << (int)e::C << " " << (char)s::A; // 2 A
}explicit: In this case I have a long article explaining this keyword. It basically avoid making implicit conversion between types. See: rrmprogramming/custom-conversions
export: Used in C++ modules to export a module See: cppreference/export
C++
// helloworld.cpp
export module helloworld; // module declaration
import <iostream>; // import declaration
export void hello() { // export declaration
std::cout << "Hello world!\n";
}
// main.cpp
import helloworld; // import declaration
int main() {
hello(); // Prints "Hello World!"
}extern: Could be used forstaticor thread storage duration variables and external linkage. Also usefull to declare template functions. Finally, the main usage is to applie the language specification in the string-literal to all function types, function names with external linkage and variables with external linkage declared. See: cppreference/extern
C++
extern "C" {
int open(const char *pathname, int flags); // C function declaration
}
int main() {
int fd = open("test.txt", 0); // calls a C function from a C++ program
}
// This C++ function can be called from C code
extern "C" void handler(int) {
std::cout << "Callback invoked\n"; // It can use C++
}F
false: Type, capable of holding one of the two values: true or false. The value ofsizeof(bool)is implementation defined and might differ from 1. See: cppreference/false
C++
bool b = false;
std::cout << b; // Prints "0"float: Floating point number with the size of 32 bits (4 bytes). Matches IEEE-754 binary32 format if supported See: cppreference/float
C++
float f = 10.0;
std::cout << sizeof(f); // 4 bytes.for: There are two ways of using for:for-loopandrange-base-for-loop. Iterates for a certain condition. See: cppreference/for
C++
for (int i=0; i<3; i++)
std::cout << "For-loop: " << i << '\n';
std::vector<int> v = {2, 4, 6};
for (int element : v)
std::cout << "Range-based: " << element << '\n';
// Output
For-loop: 1
For-loop: 2
For-loop: 3
Range-based: 2
Range-based: 4
Range-based: 6friend: Used inside a class, lets the class or function to access theprotectedandprivatefields from other class. See: cppreference/friend
C++
class A {
friend class B; // B can access A
friend void change_value(int x); // Friend function declaration
void foo() { std::cout << "A::foo()\n"; }
int valueA = 10;
};
class B {
public:
void call_A() {
A a;
a.foo(); // Can access A::foo() because A defines B as friend class.
}
};
void change_value(int x) {
A a;
a.valueA = 50; // Can acces A because its a friend function.
std::cout << "Change A.value = " << a.valueA << "\n";
}
int main() {
change_value(10);
B b;
b.call_A();
}
// Output
Change A.value = 50
A::foo()G
goto: Jumps to a defined label. See: cppreference/goto
C++
int main() {
int x = 0;
begin:
std::cout << x << '\n';
x++;
if (x == 3)
goto end;
else
goto begin;
end:
}
// Output
1
2
3I
if: Conditional statement. See: cppreference/if
C++
if (true) {
std::cout << "Condition true";
}inline: Defines that a function is implemented inline an with this identifier the function will be only inserted once per translation unit. If the function is implemented inline without the specifier, the compiler add it automatically. Since C++17,inlinecan also be used for variables. For example. See: cppreference/inline
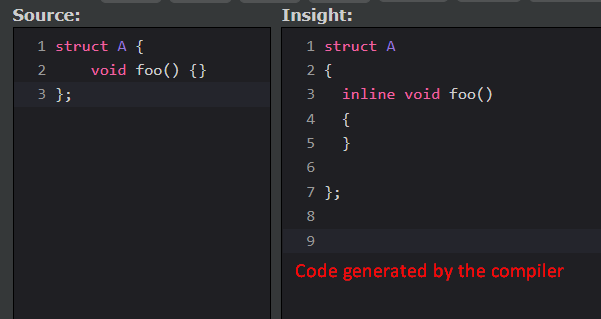
C++
struct A {
inline void foo() {
std::cout << "Inlined function";
}
}int: Integer type used for natural numbers. Guaranteed to be at least 16 bits (2 bytes) and can vary between 2-4 bytes depending on the architecture. See: cppreference/int
C++
int x = 10;
std::cout << sizeof(x); // 4 bytes.L
long: Integer type used for natural numbers. Guaranteed to be at least 32 bits (4 bytes) and can vary between 4-8 bytes depending on the architecture. See: cppreference/long
C++
long x = 10;
long int y = 10.0;
long long z = 10;
std::cout << sizeof(x); // 8 bytes.
std::cout << sizeof(y); // 8 bytes.
std::cout << sizeof(z); // 8 bytes.M
mutable: Permits modification of the class member declared mutable even if the containing object is declared const. Onlye allowed inside member-functions See: cppreference/mutable
C++
struct A {
mutable const int* x = new int(10);
mutable int y = 20;
};
int main() {
A a;
a.x = new int(50);
std::cout << "a.x = " << *a.x << '\n'; // "a.x = 50"
a.y = 200;
std::cout << "a.y = " << a.y << '\n'; // "a.y = 200"
}N
namespace: Provides an scoped name to avoid duplicate values. All definitions inside a namespace must be anotated with it. See: cppreference/namespace
C++
namespace n1 {
void foo() {};
}
int main() {
n1::foo();
foo(); // error: 'foo' was not declared in this scope; did you mean 'n1::foo'?
}new: Allocates memory on the heap. See: cppreference/new
C++
{
int y = 10; // Allocated in the stack, freed after the end of the scope.
int* x = new int(10); // Allocated on the heap, no deallocated after the scope.
}
// 4 bytes of 'y' freed.
// 4 bytes of 'x' still in use on the heap.
noexcept: Mark a function as not capable of throwing exceptions. It also can be used as operator in order to know if a function can throw exceptions. See: cppreference/noexcept
C++
void foo() noexcept { } // The function will not throw
void foo2() noexcept(false) {} // The function may throw
void foo3( void* foo() noexcept) {} // The function takes a pointer to a function that don' throw
void foo4() { }
int main(){
std::cout << noexcept(foo()); // True
std::cout << noexcept(foo2()); // False
std::cout << noexcept(foo3()); // False
std::cout << noexcept(foo4()); // False
}not: Performs a logic not operation. It is equivalent to!. See: cppreference/not
C++
bool b1 = false;
bool b2 = not b1;
if (b2 == true) {
std::cout << b2; // True;
}not_eq: Performs a logic not equal operation. It is equivalent to!=. See: cppreference/not_eq
C++
bool b1 = false;
bool b2 = not b1;
if (b2 not_eq b1) {
std::cout << "They are not equal";
}nullptr: It is a pointer literal. It is explicitly convertible to 0. See: cppreference/nullptr
C++
int* x = nullptr;
if ( x == 0 ) {
std::cout << "x is nullptr";
}O
operator: Denotates a operator overloading. See: cppreference/operator
C++
struct A {
void operator()() const {
std::cout << "A::operator()";
}
};
int main() {
A a;
a(); // Prints: "A::operator()"
a.operator()(); // Can be called this way aswell
}or: Performs a logic or operation. It is equivalent to||. See: cppreference/or
C++
if ( true or false ) {
std::cout << "At least one is true";
}or_eq: Performs a bitwise or operation with the value itself. It is equivalent to|=. See: cppreference/or_eq
C++
auto b1 = 0xb00110000;
auto b2 = 0xb00101111;
std::cout << std::hex << b1 << '\n'; // b00110000
b1 or_eq b2;
std::cout << std::hex << b1 << '\n'; // b00111111P
private: Access specifier that mark member functions and variables only visible inside the member. Structures are prublic by default and classes are private. See: cppreference/private
C++
struct A {
private:
int x = 10;
};
int main() {
A a;
a.x; // error: 'int A::x' is private within this context
}protected: The member functions and variables are only visible inside the class itself and the ones that derive from it. See: cppreference/protected
C++
struct A {
protected:
int x = 10;
};
struct B : A {
void foo() {
std::cout << x;
}
};public: Member functions and member variables are visible from outside the member aswell. See: cppreference/public
C++
struct A {
public:
int x = 10;
};
int main() {
A a;
std::cout << a.x;
}